What is a sedan? Get the answer plus more in this comprehensive sedan buying guide.
SUVs have displaced sedans as the vehicle of choice for families and single individuals alike. Yet, when most people still think of a car, they picture a four-door passenger vehicle with a protruding cargo area — they picture a sedan!
Make no mistake, despite losing its sales crown, the sedan remains a very popular vehicle class for the masses and will continue to have a place in the automotive world for years to come.
What is a sedan, how do they differ from the other types of cars, and how did they become the most popular class of vehicles for over a century? We answer these questions plus several others to help you become a more informed car buyer.
IN THIS GUIDE
What Is A Sedan?
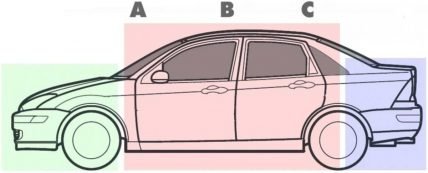
A sedan is a passenger vehicle with a three-box configuration, featuring separate components for the engine, passenger cabin, and cargo area (trunk).
The term is sometimes used to describe any vehicle with the appearance of a three-box, including those with hatchback-like cargo area and door. However, in the strictest sense, a sedan is characterized by a closed body with a fixed metal roof, four doors, two rows of seats, and a cargo area that’s separate from the passenger area.
Sedans can vary greatly in size, performance, and sophistication. They range from the small to the very large, austere to ultra-luxurious, and “soulless” to sporty.
What Does Sedan Mean?
Now that you know what a sedan is, let’s look at what the word “sedan” actually means.
The term goes way back to the sedan chair, an enclosed box with windows used to seat and transport a person of importance, with porters at the front and rear carrying it using horizontal poles. It is believed to be derived from the Italian word ‘sedia’, which means chair or seat, and sedia itself likely traces its origins to “sedere,” the ancient Latin word for “sit”.
In the U.S., Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and Latin America, cars of this configuration are called sedans, while in the UK, ‘saloon’ is the preferred terminology.
Sedans are known as ‘berline’ in France and ‘berlina’ in Italy, Spain, Portugal, and Romania. In German-speaking countries, such a vehicle is called a Limousine, and what North Americans know as Limousine is referred to as a ‘Stretch-Limousine’.
Pros And Cons Of Sedans
The sedan was the most popular type of car for over a century and continues to be one of the most popular, even though it has lost its dominance to SUVs. There is clearly something people love about these vehicles and something they find less appealing than SUVs.
Let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages of owning a sedan.
Sedan Advantages
Here are the top five reasons why sedans remain one of the most popular types of vehicles…
- Affordability: Sedans are easier and cheaper to build than nearly every other type of vehicle, making them more affordable to buyers. The lower purchase price also makes them cheaper to insure, though other factors may offset this advantage.
- Drivability: Sedans have a relatively small size and light frame that makes them easy to drive and handle in crowded spaces. They can easily navigate tight city streets and squeeze into tight parking spots.
- Fuel economy: If saving money on fuel is important to you, a sedan will give you the biggest return on investment. Their light frame, low profile, smaller engines, and wider availability of hybrid options make sedans almost always more fuel-efficient than every other type of vehicle.
- Safety: The low ride height of sedans results in a low center of gravity that greatly reduces the risk of rolling over when cornering, swerving, or changing direction at high speeds. Together with coupes, hatchbacks, and wagons, they provide the most stability while driving.
- Security: Whereas vehicles with rear hatches or tailgates require extra storage pieces to conceal valuables you don’t want visible through the windows, a sedan’s enclosed trunk allows those valuables to be locked away out of sight.
Why Buy A Sedan
There are quite a few good reasons for choosing a sedan over other classes of vehicles. If you’re interested in an affordable vehicle that offers excellent fuel-efficiency, great ride and handling, solid high-speed stability when driving, and an enclosed cargo area that discourages theft, sedans are hard to beat.
Sedan Disadvantages
No class of vehicles is perfect, and sedans are no exception. Now that you know the benefits of driving one, let’s look at the areas where they fall behind the pack.
- Space: Sedans offer less interior and cargo space than vehicles with two-box designs, such as hatchback, wagons, SUVs, and crossovers. This makes them a less versatile option for large families or those who routinely haul people and their things.
- Towing, hauling: Since they are light, small, and often have small engines, sedans are not particularly good at towing or hauling heavy loads.
- All-weather driving: If you live somewhere with bad weather (snowy, rainy, etc.), a high ground clearance and decent all-wheel-drive system can be extremely beneficial. Unfortunately, sedans sit low to the ground and most models aren’t offered with AWD.
- Off-roading: Their low ground clearance, lighter frame, and limited availability of AWD make sedans unsuitable for off-roading. Tearing up dirt trails deep in the desert or forest is generally not an option with these vehicles.
- Visibility: The low seating position of sedans gives drivers less visibility than high-riding vehicles such as SUVs, crossovers, and pickup trucks do.
Why Not Buy A Sedan
A less spacious interior and cargo area, poor towing and hauling capabilities, low ground clearance, and lack of all-wheel drive are the main reasons why droves of car buyers are shifting from sedans to SUVs.
These vehicles are not ideal for drivers who frequently haul around many people and their things, live in areas with bad weather, and/or like to tackle the rugged outdoors.
Types Of Sedans
Sedans have been produced in a wide range of configurations since the first mainstream models rolled off the assembly line over a century ago. Let’s look at the different types of sedans that have been introduced over the decades.
Notchback Sedans
Notchback sedans are distinguished by a three-box design where the roof runs parallel to the ground and the trunk (boot) is truncated, making them the archetypal sedan. They were fairly common in North American in the 1960s-1980s, but only a few models remain.
Modern examples of notchback sedans include the Chrysler 300c and perhaps the Audi A3 sedan.
Fastback Sedans
With fastback sedans, the roofline stretches to the trunk lid in one continuous slope (no hard angles). The sleek profile typically makes them more aerodynamic than notchback sedans but less space-efficient.
The arrival of the first-generation Mercedes-Benz CLS in 2004 kick-started what many consider the “four-door coupe” segment. However, you will find that the concept of a four-door coupe is simply a new marketing take on the fastback sedan.
In addition to the Mercedes-Benz CLS, other examples of fastback sedans are the Tesla Model 3, Audi A7, and Porsche Panamera, and even mainstream models such as the Honda Accord, Hyundai Sonata, and Volkswagen Arteon.
Liftback Sedans

These cars have a silhouette similar to a sedan; however, instead of a trunk lid, the entire back raises like a hatch or liftgate to access the cargo area.
While this design characteristic technically makes them hatchbacks, their three-box appearance holds enough weight to make most people consider them a sedan variant.
Liftback sedans usually have a fastback design. Popular examples include the Tesla Model S and Audi A5 Sportback.
Note: To avoid confusion, the term “hatchback sedan” is often not used since many models are offered in both hatchback and sedan body styles (e.g Honda Civic sedan and Honda Civic hatchback).
Hardtop Sedan
Popular in the United States in the 1960s through the 1970s, hardtop sedans lack a b-pillar, thus leaving a wide, uninterrupted opening spanning the full width of the front and rear side windows. The idea was to make the fixed hardtop of these sedans look like a convertible’s top.
While hardtop sedans died out in North American in the late 1970s, they remained popular in Japan through the 1990s. The 1958 AMC Ambassador Hardtop Sedan is a good example of this style.
Club Sedan
Club sedans were very popular during the 1920s through the 1950s. Typically fashioned as premium models, they had a short roofline and, therefore, less interior space than other types of sedans but made an impression with their well-appointed, upscale interiors.
Club sedans were in fact named after the club carriages in railroad trains, which provided riders with the best creature comforts such as extending chairs and a bar.
Close-Coupled Sedan
A car of the 1920s and 1930s, close-coupled sedans had rear seats that were located further forward than in other sedans of the era, a design feature that greatly reduced their overall length but made seating arrangements more cramped. They were the smallest sedans offered
If you need an example, look up the Ford Victoria of the 1930s and the early Chrysler Imperial models.
Sedan Size Classes
One of the choices you will have to make when shopping for a sedan is what size to get. People tend to think of sedans as being either mid-size or full-size, but in reality, there are a total of four sedan size classes: Subcompact, compact, midsize, and full-size.
Subcompact Sedan
The increasingly rare subcompact size class serves as an entry point for many individuals on a tight budget. Examples include the Toyota Yaris, Kia Rio, Nissan Versa.
Pros: They are the smallest and lightest, most maneuverable, most affordable, and oftentimes, most fuel-efficient sedans on the market, factors that make them good vehicles for city driving.
Cons: Subcompact sedans feel cheap due to having minimal sound insulation and a less refined interior and ride quality. Their truncated proportions tend to make them look a little dopey, while their short wheelbase can make space tight for rear passengers and cargo.
Compact Sedan
Compact sedans are where people start to feel like they’re driving a serious sedan. In Canada, Europe, and many other markets of the world, they are the most popular size class.
Good examples are the Honda Civic, Toyota Corolla, BMW 3 Series, and Mercedes-Benz C-Class.
Pros: Compact sedans manage to be a bit roomier, more refined, and more powerful than subcompacts sedan while retaining most of the drivability and fuel efficiency associated with its smaller peer. Their rear seats are usually large enough for small adults, and they are often offered with their automaker’s best safety and tech features.
Cons: Although mid-size sedans are roomier than subcompacts, large adults may still find the rear seats a bit cramped and uncomfortable on long trips. Also, although sufficient for everyday use, their cargo space isn’t’ particularly well suited for hauling big items.
Midsize Sedan
Midsize sedans have long been the heart of the sedan segment in the U.S., typically offering the best balance between spaciousness, performance, refinement, and fuel-efficiency.
The Toyota Camry, Honda Accord, Hyundai Sonata, Chevrolet Malibu, and Nissan Altima are popular examples.
Pros: The mid-size segment often represents the largest and most luxurious sedans for most non-luxury automakers, so expect some truly impressive tech, comfort, and convenience features. Their roomier interior makes long trips more comfortable for children and adults of all sizes, while their more spacious trunk allows them to haul larger items.
Despite their increased size, fuel-efficiency is among the best in the automotive industry.
Cons: The larger size of midsize sedans makes them less maneuverable than their smaller counterparts. These cars can also carry large price tags, especially in higher trims.
Full-Size Sedan
Once a popular size class, full-size sedans are a rare breed in today’s automotive landscape. Even so, they remain the flagship model for those automakers that still offer one.
Examples include the Toyota Avalon, Kia Cadenza, and Nissan Maxima on the mainstream end, and the Mercedes-Benz S-Class, Lexus LS, Audi A8 on the luxury end.
Pros: These are the largest, roomiest, and most luxurious sedans, offering ample room for rear passengers and tons of trunk space. They also showcase the best comfort and tech features the automaker has to offer.
Cons: Understandably, the large proportions and extra weight makes full-size sedans less maneuverable than their smaller peers. The extra weight necessitates bigger, more powerful engines that require more gas, while their unmatched refinement and plethora of available luxury features make them the most expensive sedans.
Sedan vs. Other Car Types

We highlighted the advantages and disadvantages of sedans and why you should or shouldn’t buy one. We’re now going to compare them to three other vehicle types — coupes, hatchbacks, and SUVs — to give you even more perspective.
Sedan vs Coupe
Coupes are two-door vehicles, while sedans have four doors. Simple, right? Not quite.
As apt as that distinction may be, the differences between the two body styles go beyond the number of doors they have.
- Passenger space: Coupes have a much shorter wheelbase than sedans, which means less passenger room. While sedans normally seat five people with ample head and legroom, coupes typically seat four at most, though their rear seats are often so cramped that they’re unusable for adults.
- Cargo space: Since sedans are longer than coupes, they offer more cargo space in the trunk for carrying packages and gear.
- Accessibility: Coupes have wider front doors than sedans do, giving front occupants more space to enter and exit the vehicle. However, the absence of rear doors makes getting in and out of the rear seats difficult.
- Performance: The shorter wheelbase and lighter curb weight of coupes allow for faster acceleration, more spirited handling, and better braking. Sedans tend to come with stronger engines to offset their larger size.
- Fuel-efficiency: Because coupes are usually designed to be sportier than sedans, their engines and transmission tend to be tuned more for performance. However, the difference in fuel-economy is often negligible if the coupe and sedan are variants of the same model.
- Styling: Most sedans emphasize a luxurious look and feel, while the shorter body and fewer doors of coupes result in a sportier, more athletic appearance. Coupes are generally considered more attractive than sedans.
- Price: Coupes are almost always more expensive than their sedan equivalents, even if they have the same engines and features. That’s because they are rarer, and buyers are willing to pay extra for their more attractive styling.
Which Should You Buy?
If you’re looking for a practical, family-friendly vehicle, the extra doors, larger seating capacity, and more capacious interior and cargo area make sedans the smarter choice.
On the other hand, if you like your cars to look striking; prefer sportier, more performance-oriented handling; and aren’t too concerned about interior space, a coupe may be the vehicle for you.
Sedan vs Hatchback
Everything you need to know about hatchbacks can be found in our comprehensive hatchback buying guide.
The essential difference between a sedan and a hatchback is the trunk. Whereas the cargo area of a sedan is a separate, enclosed compartment, the cargo area of a hatchback is opened to the passenger area and is accessed via a roof-hinged hatch.
Let’s see what that entails and how the two body styles compare to each other.
- Passenger space: Similarly-sized hatchbacks and sedans typically offer the same amount of interior roof. However, their higher roofline of hatchbacks may result in rear passengers enjoying more headroom.
- Cargo space: Because of their tow-box design and the open nature of their cargo area, hatchbacks will have significantly more cargo room than their sedan equivalents, especially when the rear seats are folded.
- Visibility: Depending on how many things you have in the cargo area, hatchbacks offer drivers better visibility because of their large rear windows. Both body styles provide the same amount of front and side visibility.
- Drivability: Hatchbacks tend to be shorter in length than sedans, which combined with their better rear visibility, makes driving and parking a little easier.
- Performance: Because sedans and hatchbacks are usually different body styles of the same model, performance is nearly identical between the two. They come equipped with the same engines and offer the same capabilities on and off-road.
- Fuel efficiency. Sedans are typically more fuel-efficient than hatchbacks because they are lighter and more aerodynamic. However, the difference can be negligible.
- Price: In Europe, where hatchbacks are very popular, the price difference between the two body styles can be small. In North America, hatchbacks are rarer and are usually only available in higher-spec trims. Car shoppers have far fewer affordable options to choose from.
Which Should You Buy?
Your decision to buy a sedan or hatchback will mostly boil down to how much cargo space you need. Although sedans are a little bit more fuel-efficient and offer buyers more affordable options to choose from, hatchbacks offer significantly more cargo space because of their higher roofline and the open nature of their cargo area.
They are also a little easier to drive because of their shorter length and better rear visibility.
Sedan vs SUV
Learn more about SUVs in our detailed SUV buying guide.
With consumers flocking to SUVs in droves, you’d think there is something seriously wrong with sedans. Not so!
Choosing between the two vehicle types can be difficult once you dig into the advantages and disadvantages of each one.
- Space: SUVs have a tall, box-shaped body that grants them significantly more cargo room than sedans. Passengers may enjoy more headroom due to their higher roofs, and you can certainly carry bigger and more things.
- Seating capacity: SUVs can offer three rows of seats and accommodate up to eight passengers, while sedans max out at two, with enough room for five passengers.
- Visibility: With a higher driving position and larger side and rear windows, SUVs provide drivers greater visibility of their surroundings.
- Drivability: Sedans are smaller, sit lower to the ground, and are less top-heavy than SUVs, making them much easier to drive, maneuver, and park.
- Capability: SUVs are more capable vehicles than sedans. Their stronger frames, greater curb weight, and more powerful engines allow them to carry and tow heavier loads, while their high-ground clearance and all-wheel-drive configurations (most sedans don’t offer AWD) make them better for inclement weather and off-road driving.
- Fuel efficiency: Sedans are smaller and lighter than SUVs and therefore require less power and fuel to move. They are more fuel-efficient on average.
- Safety: Sedans have a low ride height compared to SUVs, giving them a lower center of gravity that reduces the risk of rollovers. On the other hand, the larger size and mass of SUVs allow them to better absorb impacts, providing better protection for occupants in head-on collisions with smaller vehicles.
- Price: SUVs tend to be more expensive than sedans, even when they are in the same size class and have the same engine and features. In other words, you will get more features with a sedan than you will with a similarly-priced SUV.
Which Should You Buy?
If you need space for more passengers and their gear, tow frequently, and/or live in an area with bad roads and weather, an SUV will be a smart choice. If you prioritize driving comfort, fuel economy, and maneuverability, getting a sedan may be the way to go.
History Of The Sedan
Some sources suggest that the first sedan in the automotive sense was the 1899 Renault Voiturette Type B, a two-seat car with a roof and an extra external seat for a footman or mechanic, while others give the title to the 1911 Speedwell, the first four-seat, fixed-roof automobile to actually use the term.
Whatever the case, it probably wasn’t until the arrival of the Studebaker Four and Studebaker Six in 1912 that the word ‘sedan’ went mainstream. Hundreds upon hundreds of sedan models have come and gone since then, with some changing the automotive landscape for the better.
The first-generation Toyota Prius, for instance, was the first commercially available hybrid car, set the stage for a new breed of hybrid vehicles, and made electrified vehicles mainstream. More than that, the Prius bridged the gaping gap between ICE and full-electric vehicles and made motorists warm up to the idea of an electric future.
Next up was the Tesla Model S. While by no means the first all-electric car ever made, it was the first one that could be driven like a regular car without having to worry about range anxiety and the first to become a best-seller in a car segment (the large premium sedan class).
The success of the Model S pushed every automaker to take the transition to electric powertrain more seriously. It helped launch the EV revolution, paving the way for another Tesla sedan, the more affordable and accessible Model 3, to catapult the automotive world towards a truly electric future.
Today, sedans offer the widest variety of powertrains of any vehicle type. They continue to evolve to better accommodate the needs of drivers and passengers, offering more capability and versatility than ever before.
So, while small crossovers and SUVs have become the ride of choice for many car buyers, the lighter, more fuel-efficient, and easier to drive sedan remains a competitive and compelling option.
What is a sedan? Think of it as a car of the ages and a bearer of innovation and revolutionary change.
Sedan FAQs And Answers

When putting together our detailed sedan buying guide, we made sure to give you all the information you need to shop for one with confidence. If you didn’t have time to go through the entire guide, the following FAQs and the answers to them highlight many of the key points we touched on.
Are Sedans Good Cars?
Yes! If sedans weren’t good cars, they wouldn’t be the best-selling class of vehicles in automotive history.
Even though comparably-sized crossovers and SUVs offer a higher seating position and more passenger/cargo space, sedans are a more efficient means of transporting four or five people. They are lighter, easier to drive, and more fuel-efficient vehicles.
Are Sedans Dead? Are Sedans Disappearing?
While traditional sedans have been replaced by crossovers and SUVs as the most popular type of vehicle, we firmly believe there will always be a place for them in the market.
Not only are SUVs noticeably more expensive and less attainable for the average car buyer, but there will always be people who simply prefer the design, affordability, fuel-efficiency, and maneuverability that sedans offer.
Should I Buy A Compact, Mid-Size, Or Full-Size Sedan?
The decision to buy a compact, midsize, full-size sedan will mostly boil down to how much space you need. If interior and cargo space is a big priority, get a midsize or full-size sedan. If not, consider their other features.
Compact sedans trade space for a lower price, better maneuverability, and superior fuel efficiency, while full-size sedans give you more space and premium features in exchange for a higher price and the lowest fuel economy of the trio. Mid-size sedans strike a balance between the two size classes.
What Sedans Hold Their Value?
If you’re looking for a sedan with a good resale value, models from Japanese automakers, particularly Toyota and Honda, hold their value the best. Buyers are willing to pay more for a used Toyota Camry or Honda Accord than competing models because they’ve long been associated with reliability and typically last longer.
Are Four-Door Coupes Real Sedans?
Four-Door Coupes are vehicles that combine the stylish, swept-back profile of a two-door coupe with a sedan’s four-door practicality. Some are sedans in the traditional sense, while others are hatchbacks.
Models that have a sealed trunk fit the technical definition of a sedan, while those with cargo areas opened to the cabin and roof-hinged liftgates (liftback sedans) are technically hatchbacks, though most people consider them sedans because of their outward appearance.
Conclusion
When it comes to cars, no other class of vehicle has dominated our streets, garages, and parking lots for as long as the sedan has. This four-door passenger car has defined the automotive industry ever since it first came along in the early 20th century and will continue to stand the test of time despite its declining popularity.
And why not? Sedans are very affordable, easy and safe to drive, very good on fuel, and inexpensive to own, a combination of qualities you simply won’t get with SUVs or most other types of vehicles.
So, what is a sedan? In the technical sense, it is a four-door car with a three-box design that houses the engine, passengers, and cargo in separate, sectioned-off compartments. The broader definition also includes cars that have a shape reminiscent of a three-box design but with the cargo area connected to the passenger cabin (e.g. liftback sedans).

